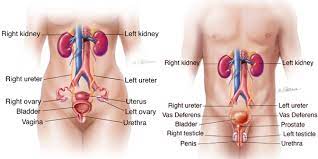
Urinary tract infections are more common in women. They usually occur in the bladder or urethra, but more serious infections involve the kidney.A bladder infection may cause pelvic pain, increased urge to urinate, pain with urination and blood in the urine. A kidney infection may cause back pain, nausea, vomiting and fever.Common treatment is with antibiotics.
If you’re a woman, your chance of getting a urinary tract infection is high. Some experts rank your lifetime risk of getting one as high as 1 in 2, with many women having repeat infections, sometimes for years. About 1 in 10 men will get a UTI in their lifetime.
Here’s how to handle UTIs and how to make it less likely you’ll get one in the first place.
Symptoms of UTIs
The symptoms of a UTI can include:
- A burning feeling when you pee
- A frequent or intense urge to pee, even though little comes out when you do
- Cloudy, dark, bloody, or strange-smelling pee
- Feeling tired or shaky
- Fever or chills (a sign that the infection may have reached your kidneys)
- Pain or pressure in your back or lower abdomen
Types of UTIs
An infection can happen in different parts of your urinary tract. Each type has a different name, based on where it is.
- Cystitis (bladder): You might feel like you need to pee a lot, or it might hurt when you pee. You might also have lower belly pain and cloudy or bloody urine.
- Pyelonephritis (kidneys): This can cause fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, and pain in your upper back or side.
- Urethritis (urethra): This can cause a discharge and burning when you pee